This year, the health and fitness theme has rocketed with a boost of wearable technology and all kinds of other sensory devices that help enhance physical abilities. In 2013, food brands became more health-conscious, design labels sought for solutions to make physical activity and moderate eating experiences more sophisticated, and tech brands channeled their expertise into making pieces that extend the limits of what a human body can do.
Below, there are six major trends, along with sub-trends, that have been mainstreaming in this field throughout 2013.
Physical disability as incentive to innovate
Physical illnesses are now positioned not as an end of the life journey but rather as a transition to a whole new level. The lack of ability to do something in a traditional way is now perceived as a gap that is to be filled with new solutions based on a creative technological approach. Tech-powered projects are emerging fast to support physically challenged individuals in the process of overcoming the boundaries.
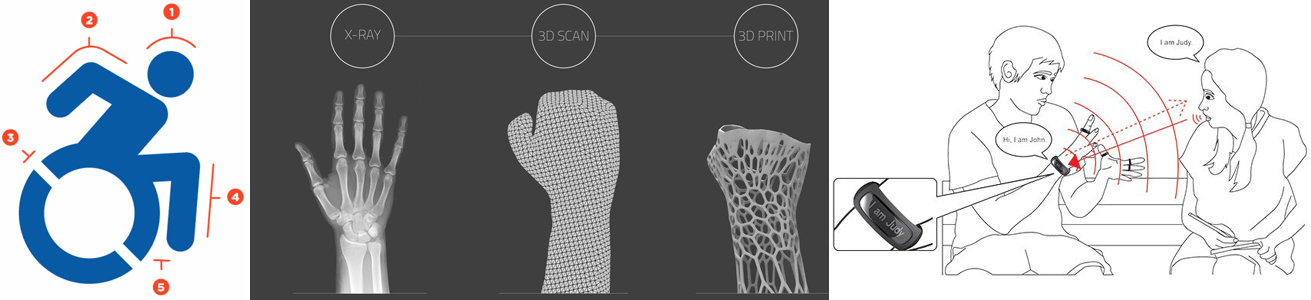
Left to right: 1. The active accessible icon 2. Cortex 3. Sign Language Ring
- Image of a disabled person gets a positive facelift. This year, some cities across the USA, including NYC, agreed to adopt a new, energy-packed sign that symbolizes wheelchair accessibility. Guinness launchedan emotional heartwarming video featuring a team of friends in wheelchairs who are playing basketball. In the end of the ad, five of six friends get up except one, a guy with a physical disability who stays in the chair. After the game, all of them go to a pub to celebrate their friendship with beer.
- Prosthesis as a technological masterpiece. The rapid development of bionic technologies allows to create artificial body parts that look similar to the real ones and offer similar level of performance. In February, Channel 4 aired a documentary titled “How to Build a Bionic Man” that explores the innovation in this field—on the dedicated site, one can also bionicise their body online. Mind-controlled prosthesis start a new era in the niche, bringing new possibilities to people who don’t have limbs. 3D-printing technologies allow to reduce the time and cost of creating artificial body parts—from arms to eyes—and also can be used in creating chick casts for fractured bones, like Cortex.
- Improving the damaged sensory experience. The blind people are getting a chance to experience the world in a better way with a range of new devices. These include the Kinect Eyes-Free yoga instructor that analyzes the movement and gives audio instructions, and also the UltraBike ultrasound sensor kit that enables visually impaired people to ride a bicycle and “see” the obstacles. Bikes get equipped with special device featuring sensors that detect various objects ahead and alert the rider through vibrating handlebars. Yahoo! created a dispenser that creates 3D replicas of everyday objects for blind kids—children name the objects they would like to touch, and the machine produces the tiny copies of these items right away. The Sign Language Ring allows deaf people to communicate freely with any person—the rings analyze the moves of fingers and then translate the words and phrases into an audible form through a special bracelet.
What to expect: From the practical point of view, disability coupled with technology now means even more than ability in its basic form. With the rise of bionic science and easy-to-create 3D body parts, it’s possible to deliver missing body limbs and organs that are almost as good as original ones. With the development of transport technology and sensory devices, physically challenged people can get the same amount of activity as healthier people. Mind-controlled prosthesis and other devices are to dominate in the life of people who lost physical ability, partly or completely. A human body becomes a strategic design and technology project of the coming years.
To sum up, the year of 2013 can be characterized by the boost of conscious food consumption (eating less, opting for healthier food), tracking all body signals (both physical and mental), and the rise of technology aimed to drive more ability into the live of the handicapped.